Main Text starts here.
Corporate Information
Business Risks and Other Risk Factors
Business Risks and Other Risk Factors
Disclaimer
This translation does not constitute a solicitation for investments in the stocks and other securities issued by the companies of the Japan Post Group, regardless of whether in Japan or overseas.
UNOFFICIAL TRANSLATION
The following is an English translation of “Business Risks and Other Risk Factors” described in the Annual Securities Report (19th term), which is provided only in Japanese.
Although Japan Post Insurance pays close attention to providing an English translation of the information disclosed in Japanese, the Japanese original prevails over the English translation in the case of any discrepancy.
This text is based on the judgment of the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries (hereinafter referred to as “the Group”) as of the filing date of the 19th Annual Securities Report, unless otherwise stated.
Risk management systems and processes for identifying and managing business risks and other risk factors, etc.
In accordance with the “Basic Risk Management Policy,” we have set up and regularly convene the Risk Management Committee headed by the Chief Risk Officer (CRO), while formulating rules of risk management.
The Risk Management Committee deliberates on risk management policies and matters concerning the establishment and operation of risk management systems as well as on matters concerning the implementation of risk management. This committee also performs appropriate risk management by monitoring and analyzing the status of each risk and other related matters. The CRO submits and reports on important matters to the Executive Committee, the Audit Committee, and the Board of Directors for discussion. (details stated in “IV. Status of Submitting Company, 4. Corporate Governance, etc., (1) Overview of corporate governance, ③. Other matters regarding corporate governance, b. Status of establishment of risk management systems” of the 19th Annual Securities Report).
Among the matters related to business conditions, accounting conditions, etc., described in the Annual Securities Report (19th term), business risks and other risk factors are referred to as major risks that management believes may have a significant impact on the Group’s financial position, operating results, cash flow status, and indicators such as EV (embedded value) of corporate value and ESR (Economic Solvency Ratio) of soundness. The most significant risks and risks recognized to have been increasing in awareness through FY2025 or to increase in awareness in FY2025 are identified after considering the degree of impact and the possibility of the occurrence and managed throughout the fiscal year. In classifying such risks and describing the information related to each one, we conducted a questionnaire (hereinafter referred to as the “Management Questionnaire”) regarding business risks and other risk factors directed at members of the Executive Committee as of March 31, 2025, who were executive officers at or above the level of managing executive officer and those in charge of business operations as of March 31, 2025, in order to appropriately reflect the Company management’s awareness of the impact, possibility of occurrence, and countermeasures. Based on the aggregate results, the Risk Management Committee and the Executive Committee discussed the results and listened to the opinions of Outside Directors. The risk items are also reassessed through the said questionnaire.
Risk map and most significant risks, etc.
Risk map
The risk map of business risks and other risk factors formulated based on the aggregate results of the Management Questionnaire and in consideration of the impact and possibility of occurrence of risks is as follows. Risks that fall under the categories of “high” impact and “high” possibility of occurrence, “high” impact and “medium” possibility of occurrence, and “medium” impact and “high” possibility of occurrence (individual risk items included in the red box on the risk map) are recognized as the most significant risks of the Company. The importance of risk items changes in the order of the most significant risks (individual risk items included in the red box on the risk map), risks that fall under “medium” impact and “medium” possibility of occurrence, and “medium” impact and “low” possibility of occurrence (individual risk items included in the yellow box on the risk map), and risks that fall under “low” impact and “low” possibility of occurrence (individual risk items included in the blue box on the risk map).
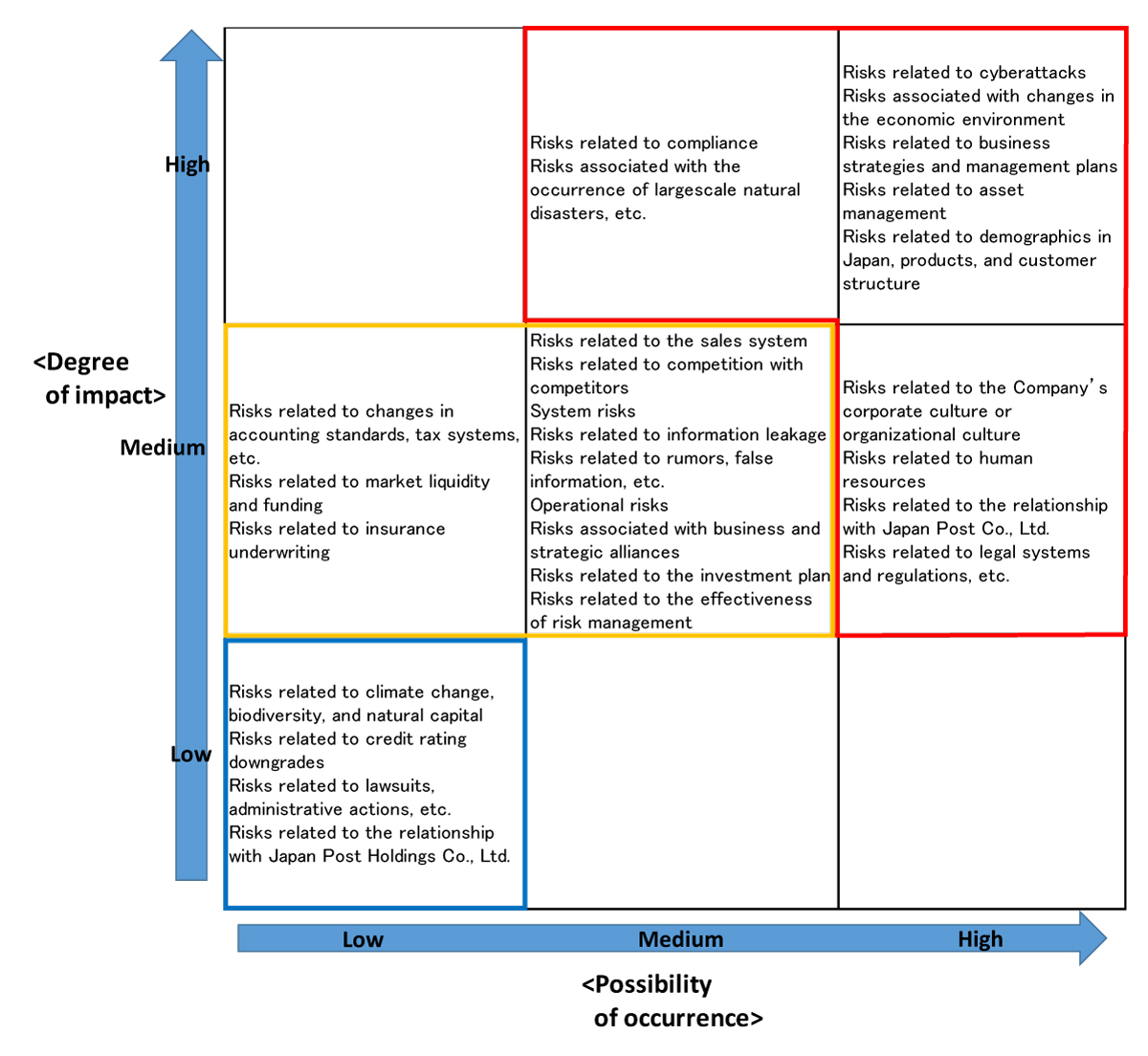
Most significant risks
Business risks and other risk factors selected as the most significant risks as a result of discussions by the Risk Management Committee based on the Management Questionnaire are as follows. In addition to risks related to business strategies and management plans, risks related to cyberattacks, which are expected to have a significant impact on the Company’s financial position, operating results, and other matters if they materialize, risks associated with changes in the economic environment, risks related to asset management, risks related to legal systems and regulations, etc. are included.
| Importance category | FY2025 |
|---|---|
| Most significant risks | Risks related to cyberattacks |
| Risks associated with changes in the economic environment | |
| Risks related to business strategies and management plans | |
| Risks related to asset management | |
| Risks related to the Company’s corporate culture or organizational culture | |
| Risks related to human resources | |
| Risks related to the relationship with Japan Post Co., Ltd. | |
| Risks related to demographics in Japan, products, and customer structure | |
| Risks related to legal systems and regulations | |
| Risks related to compliance | |
| Risks associated with the occurrence of largescale natural disasters, etc. |
Risks recognized to have been increasing in awareness through FY2025 or to increase in awareness in FY2025
Also, business risks and other risk factors selected as risks recognized to have been increasing in awareness through FY2025 or to increase in awareness in FY2025 are as follows. Risks related to asset management and risks related to human resources are included considering the recent changes in the external environment, and risks related to legal systems and regulations, etc. and risks related to the relationship with Japan Post Co., Ltd. are included in light of the incidents regarding improper handling of non-public financial information and solicitation of sales of the lump-sum payment whole life insurance before regulatory approval within the Japan Post Group announced in FY2024.
| Risks recognized to have been increasing in awareness through FY2025 or to increase in awareness in FY2025 | Risks related to asset management |
|---|---|
| Risks related to legal systems and regulations | |
| Risks related to human resources | |
| Risks related to the relationship with Japan Post Co., Ltd. | |
| Risks related to cyberattacks |
Individual risk items
Each risk item is categorized and described according to its characteristics as I. Management strategies, II. Finance/asset management, III. Business-specific, IV. Operation, and V. Others.
Ⅰ Management strategies
(1) Risks related to business strategies and management plans
-
Based on our reflections on the incidents that occurred in FY2019, such as those related to the policy rewriting that was not in line with customers’ intentions and caused disadvantages, and those in which violations of laws and regulations or internal rules were recognized (hereinafter referred to as the “solicitation quality issues”), we have formulated business strategies and management plans with an aim to achieve sustained growth by reinventing ourselves as a company truly trusted by customers. These include a Medium-Term Management Plan (FY2021 – FY2025) and the Review of Medium-Term Management Plan (FY2021 – FY2025), formulated in May 2024 to reflect changes in the internal and external environments and the progress we have made so far. In addition, incidents regarding improper handling of non-public financial information and solicitation of sales of the lump-sum payment whole life insurance before regulatory approval within the Japan Post Group have been identified in FY2024, and we strongly realize again the need for thoroughly implementing customer-oriented activities and ensuring full compliance with laws and regulations, etc.
The various risks described in “Business Risks and Other Risk Factors” are inherent in the initiatives included in the business strategies and management plans. In addition, there is a possibility that there will be increased risks or new risks that may hinder the implementation of the above initiatives by the Company in the future. In addition, these business strategies and management plans have been prepared based on a number of assumptions, including general economic conditions such as market interest rates, foreign exchange rates, stock prices, and the business environment, as well as legal systems. However, if these assumptions are not met, or if the business evaluation of each measure is not sufficiently conducted and the results are not commensurate with the investment amount and costs, it may be impossible to achieve the goals of the business strategies and management plans, which may affect the performance and financial position of the Group.
Of the risks inherent in the various measures set forth in the Medium-Term Management Plan and risks related to the assumptions made when formulating the Medium-Term Management Plan, those that are particularly important are as follows.
① Risks related to the Company’s corporate culture or organizational culture
In December 2019, the Special Investigation Committee regarding the issues related to the solicitation quality of Japan Post Insurance products, consisting of three lawyers who have no vested interest in Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd., Japan Post Co., Ltd., or the Company, released an investigation report regarding the investigation of the facts and causes of the solicitation quality issues. The report pointed out the existence of a corporate culture or organizational culture in the Group, such as postponing the investigation and resolution of causes when risk events are detected, trivialization of problems, and lack of horizontal cooperation among departments and blocked communication of information under the top-down system. The Group is working to foster a sound corporate culture under the leadership of management, and in its Medium-Term Management Plan, the Group aims to become a company where all officers and employees are able to grow with the company and can work with confidence and pride, and continue to make steady improvement. However, incidents regarding improper handling of non-public financial information and solicitation of sales of the lump-sum payment whole life insurance before regulatory approval have been identified within the Japan Post Group. If initiatives to improve the corporate culture and organizational culture, including measures to prevent recurrence of such incidents, are not successful, or they take longer than expected before they are successful, similar incidents may recur, which may affect the Group’s social credibility, performance, and financial position.
-
② Risks related to the sales system
The Company’s sales strategy calls for our consultants and post office counter sales personnel to be a reliable and friendly advisor for each customer and be selected by them through continuous provision of peace of mind across life stages and generations to retain and increase the policies in force. Specifically, we work to understand diverse customer needs and expand our product lineup to meet those needs by enhancing the after-sales follow-up services in both quality and quantity.
In sales activities, we are working to develop our employees who can propose solutions tailored to the problems of customers based on careful information gathering and understanding of their intentions, customer-oriented product proposals, and careful and easy-to-understand explanations based on the “Kampo Sales Standard” which are action principles for insurance sales. We are also involved in training employees of the post offices of Japan Post Co., Ltd.
Under this sales system, we continue to take initiatives to develop medium- to long-term sales capabilities by enhancing high-quality after-sales follow-up services through the adoption of the account manager system in FY2022 and increasing our product lineups that meet our customer needs by revising educational endowment insurance and launching sales of lump-sum payment whole life insurance in FY2023. As a result, new policies increased in FY2024, and the decline in the policies in force, which are the source of revenue, was moderate. However, if these efforts are not successful or this trend continues for a longer period of time, such as if the results of new policies do not progress as expected, the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be affected.
-
③ Risks related to demographics in Japan, products, and customer structure
Since the mid-1970s, the birth rate in Japan has generally been on a gradual downward trend and is currently among the lowest in the world. The National Institute of Population and Social Security Research estimates that the total population and the population between the ages of 15 and 64 will continue to decline, and we believe this trend is a major factor in the decline in the total amount of life insurance policies in force in Japan. In addition, the Company’s customer base is heavily weighted toward middle-aged and elderly people and women, with a relatively low proportion of young and working-age customers.
The products we handle include a high proportion of life insurance for individuals, especially savings-type products such as endowment and whole life insurance. In addition to the aforementioned long-term demographic trends in Japan and other factors, the level of domestic employment and household income, savings and investment stance, the relative attractiveness of other alternative products, the financial soundness of insurance companies, and public perceptions of social trust are affecting the number of new policies and the termination rate of policies in force.
The company is working to understand the various needs of customers of all ages, including young and working age, and to expand our product lineup to respond to their needs, for example, in April 2023, in response to the recent rise in education expenses and requests from customers, we revised Hajime no Kampo, an educational endowment insurance, and in January 2024, began offering lump-sum payment whole life insurance, Tsunagu Shiawase, to meet the needs of middle-aged and elderly customers for lifetime death benefits. However, if these efforts do not progress as expected, the Group’s business, performance and financial position may be affected.
-
④ Risks associated with business and strategic alliances
The Group has entered into alliances with other companies for various operations to create new business opportunities. When entering into alliances with other companies, etc., we execute them upon identifying risks by utilizing outside experts as necessary and establishing the Company’s management system. After entering into alliances, we ascertain the management and financial situations of our investments and partners and work to prevent risks from materializing. However, if problems arise in the execution of business by alliance partners, or if the business is not conducted as planned, or if the expected results from the business alliances are not achieved, the Group’s business, social credibility, performance, and financial position may be affected.
In addition, in June 2023, we entered into a strategic partnership agreement with KKR & Co. Inc. and Global Atlantic Financial Group making a considerable investment in the reinsurance co-investment vehicle sponsored by Global Atlantic Financial Group. In May 2024, to diversify our revenue sources and strengthen asset management capabilities, we reached an agreement on a capital and business alliance with Daiwa Securities Group Inc. and its consolidated subsidiary Daiwa Asset Management Co., Ltd., underwrote a third-party allocation of shares of Daiwa Asset Management Co., Ltd. in October 2024, and acquired 20% of the shares after the capital increase. Accordingly, the amount equivalent to goodwill has been recognized from the end of the third quarter of the fiscal year ended March 31, 2025, with 33.6 billion yen recorded as the amount equivalent to goodwill at the end of the fiscal year.
If the performance or financial position of an investee, etc. deteriorates, or the results are not commensurate with the investment amount, impairment losses may be recognized, which could affect the business, performance, and financial position of the Group.
-
⑤ Risks related to climate change, biodiversity, and natural capital
Recognizing the risks and opportunities posed by climate change, the Company expressed its support for the recommendations of the TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures) in April 2019, and is further promoting its initiatives up until now related to climate change and enhancing information disclosure (details stated in “2. Basic Concept and Initiatives on Sustainability” of the 19th Annual Securities Report).
Climate change has the potential to affect the Company’s performance and financial position, and the Company conducts scenario analysis to assess its impact.
We recognize that the main impacts of climate change on our life insurance business include possibilities of a rise in insurance claim payment due to increased damage from natural disaster, etc., and a rise in insurance claim payment due to changes in mortality and morbidity rates over the medium to long term due to the impact of rising average temperature and abnormal weather. In addition, as major impacts on asset management, we recognize impaired value of investment and loan assets due to expanding loss incurred by investees or borrowers upon increased damage from natural disasters, etc., and impaired value of investees or borrowers due to the impact of changes in regulations in line with the shift to a low-carbon society, stricter regulations and changes in consumer preference.
In addition, in order to manage our investment portfolio based on GHG emissions, we measure and analyze GHG emissions of our investment portfolio and, taking into account the analysis results, engage in constructive dialogue (engagement) with investees or borrowers, and actively promote investment and financing in renewable energy facilities.
Furthermore, we are promoting initiatives for biodiversity and natural capital which are priority issues on the global level along with climate change. We support the philosophy of the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD), a global initiative to establish an information disclosure framework related to natural capital, and joined the TNFD Forum to support its activities in June 2023, expressed our intention to make disclosure based on TNFD recommendations as an Early Adopter, on the TNFD website in December 2023.
We recognize the main impact on our life insurance business,including the possibility of a rise in insurance claim payment due to wide spread, etc. of infectious diseases from the collapse of ecological balance as well as the Company’s data centers experiencing operational delays or suspension from various natural disasters.
In terms of asset management, the Company recognizes the risk of impaired value of investment and loan assets due to the depletion of natural capital on which investees or borrowers depend, as well as the risk of impaired value of investment and loan assets due to stricter laws and regulations regarding environmental protection and changes in social demands.
We are conducting analysis on nature-related dependencies and impacts of our investment portfolio, and reflecting its results and consideration for social demands in our asset management activities.
In this manner, we are implementing various initiatives related to climate change, biodiversity, and natural capital; however, if these measures are deemed insufficient, the Group’s reputation in the capital markets and other social evaluation may deteriorate, which may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
-
⑥ Risks related to human resources
In order to conduct its business as a life insurance company, the Group requires talented personnel with a high level of expertise and stable administrative performance in each field, including insurance sales, actuarial, asset management, and risk management. In addition, with the recent evolution and spread of digital technology, we recognize that securing and training human resources to promote digital transformation (hereinafter referred to as “DX”) is a pressing issue. However, under the increasing competition for securing human resources mainly due to the impact of the declining birthrate, hiring the quality and quantity of human resources expected by the Company is becoming more difficult.
Even if hiring is successful, we may not be able to train and retain such human resources. In addition, failure to provide attractive working conditions and workplace environment, personnel affairs, work management, harassment, and other personnel and labor problems, as well as health and safety management problems in the workplace may result in an outflow or shortage of human resources.
Under the Medium-Term Management Plan, the Group aims to become a company where all officers and employees are able to grow with the company and can work with confidence and pride. Under this policy, the Group is working to revitalize communication between management and employees, support diverse career development and strengthen management capabilities, upgrade the personnel evaluation system, and reform work styles to achieve diverse and flexible work styles by promoting independent improvement activities and establishing telework (details stated in “2. Sustainability Philosophy and Initiatives” of the 19th Annual Securities Report).
In this manner, we are working to improve the motivation and satisfaction of our employees, curb the number of retirements, and develop human resources who will lead the future of the Company, thereby laying the foundations for the realization of reconstruction and sustainable growth as stated in our Medium-Term Management Plan. However, in the event that these efforts are not successful or take longer than expected to be successful, customer service quality may deteriorate, which could lower the relative competitiveness of the Group or decrease new policies or policies in force, and therefore the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be affected.
-
⑦ Risks associated with changes in the economic environment
Because most of the revenues of the Group’s businesses are generated in Japan, domestic economic and price situation, household income trend, savings and investment stance, etc., may affect the businesses conducted by the Group. Furthermore, while the global economy continues to grow moderately in general, in addition to concerns about economic recession, the economy is facing the emergence of geopolitical risks such as conflicts among nations, uncertainties concerning the policy management of the new administration in the U.S., etc., leading to further concerns about the domestic economy. In this manner, trends in these and other economic and price conditions may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
Consumer prices are rising moderately under the continued rise in service prices due to the tight labor supply and demand, rising wages, and other factors, in addition to the effect of the price pass-through originating from the previous rise in import prices. If such situations continue beyond our assumptions, concerns will arise about soaring expenses, deterioration in the profitability of insurance premiums from such expenses, difficulty in securing human resources, etc. In addition, if the interest rate level rises even more due to the rise in prices, etc., in addition to the emergence of domestic interest rate risk in asset management, cancellation and transfer of policies may increase with policy holders shifting their funds to other financial products to which they can obtain higher returns. Through such a course, the inflation trend in the domestic economy may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
-
⑧ Risks related to competition with competitors
The Company faces intense competition in the Japanese life insurance market from domestic life insurance companies, foreign life insurance companies, and various cooperative associations, and recently some of these companies have gained an advantage over the Company with respect to product content and lineup, sales channels, and insurance premium levels. With insurance companies established in the form of a joint-stock company and in the form of a mutual company coexisting and competing, there is a possibility that competitors will become more competitive in the future through consolidation and restructuring with eyes focused on overseas insurance markets, alliances with other industries, or the development of attractive products and services based on new technologies (AI, generative AI, etc.). Furthermore, if we expand the scope of our business, or if the market structure changes due to factors surrounding the Company such as deregulation or new entrants into the market, new competitive relationships may emerge with companies with which we currently have no competitive relationship. In this manner, competition with competitors may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
We are working to shift to a business model that places customer experience (hereinafter referred to as “CX”) as its foremost priority, such as by increasing customers through impressive services at its core for sustainable growth. In improving CX, we are actively promoting DX and, in promoting DX, advancing the use of AI. However, if AI develops and spreads more than we expect in the future, and our AI-based business development, operational efficiency, and improvement in productivity lack to be in line, we may fall behind our competitors, and the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be affected.
-
⑨ Risks related to the investment plan
The Company as a whole will make investments of approximately 120 billion yen, including promoting DX, during the period of the reviewed Medium-Term Management Plan. These investments will be expensed over the next few years through depreciation, and considerable costs are expected for their management and maintenance. If results commensurate with the investment amount or costs are not achieved, targets under the Medium-Term Management Plan will not be met and the Group’s performance and financial position may be affected.
-
⑩ Risks related to credit rating downgrades
The Company has obtained credit ratings from Rating and Investment Information, Inc. (R&I), Japan Credit Rating Agency, Ltd. (JCR), and S&P Global Ratings Japan Inc.(S&P), and as of March 31, 2025, the Company’s credit ratings were “AA-“(insurance claims paying ability), “AA” (ability to pay insurance claims rating), and “A+” (insurer financial strength ratings), respectively, and the Company believes it has received a favorable evaluation in its financial soundness. Under the Medium-Term Management Plan, we are thoroughly implementing customer-first business operations and striving to regain trust. However, if the performance of new policies, maintenance of policies in force, and control of operating expenses do not progress as planned, and if the credit rating of each company is downgraded due to deterioration in the Company’s future financial outlook, the Group may not be able to obtain favorable debt financing in the capital markets, and this may cause uncertainty about the Company, leading to a decrease in new policies and policies in force. In this manner, the Company’s credit ratings from the respective rating agencies may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
Ⅱ Finance/Asset management
(1) Risks related to insurance underwriting
-
① Risks related to premium setting and the accumulation of policy reserves
The Company sets insurance premiums based on the following basic calculation rates (assumed mortality rate, assumed interest rate, and assumed rate of expenses), taking into consideration the type and nature of insurance, the age and gender of the insured at the time of entering the policy, and the amount of insurance.
Assumed mortality rate Based on historical statistics, the number of deaths by gender and age is projected, and the premiums necessary to pay future insurance claims, etc. are set. The projected mortality rate used for this calculation is called the assumed mortality rate. Assumed interest rate The premiums are set by discounting a certain amount of expected return from investment of assets in advance. This discount rate is called the assumed interest rate. Assumed rate of expenses Premiums are set based on a predetermined amount of expenses required for the insurance company’s business operations. This rate is called the assumed rate of expenses. In insurance policies, if the actual mortality rate exceeds the predetermined assumed mortality rate, if the actual investment yield falls below the predetermined assumed interest rate, or if the actual expenses exceed the predetermined assumed rate of expenses, the total amount of claims and expenses to be paid will exceed the total amount of premiums and other benefits received during the insurance period, which may cause losses and affect the Group’s performance and financial position.
In accordance with the Insurance Business Act and related business regulations, the Company sets aside a significant portion of its premium income as a policy reserve for future payments of insurance claims and other benefits. Policy reserves represent the largest portion of the Company’s liabilities and are calculated based on certain assumptions regarding the frequency and timing of covered events, the amount of claims and other payments, and the amount of assets under management for each policy. If actual results deviate from these assumptions, or if future deviations are expected due to changes in the environment, an additional policy reserve may be required, which may affect the Group’s performance and financial position.
In addition, regulations concerning the accumulation of policy reserves, standard interest rates and standard life tables are set by the Financial Services Agency, the financial regulator, and any change in these factors may require a revision of premiums and additional policy reserves, which may affect the Group’s performance and financial position.
-
② Risks related to reinsurance
The Company has entered into reinsurance contracts to reduce insurance underwriting risk and asset management risk by reinsuring high-interest whole life annuity insurance policies from before privatization, in an aim to improve future earnings and capital efficiency. While we select insurance companies who meet the credit criteria set by the Company as reinsurers, if counterparty risks materialize in the future, the Group’s performance and financial position may be affected.
(2) Risks related to changes in accounting standards, tax systems, etc.
-
Deferred tax assets of the Company are recorded in accordance with current accounting standards and tax systems to the extent that future tax amounts are allowed to be reduced by the taxable income estimated based on certain assumptions. Accordingly, if the trend continues for a longer period of time in which the actual results of new policies do not progress as expected, or if significant deterioration of the economic environment continues, changes in the assumption of estimation or reductions in tax rates due to tax system reforms may lead to a decrease in the amount of deferred tax assets, which may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
In June 2020, the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) issued the amendments to International Financial Reporting Standards (hereinafter referred to as “IFRS”) 17, “Insurance Contracts,” which is effective for fiscal years beginning on and after January 1, 2023. Because this standard values insurance contracts at their economic value, fluctuations in each period may affect net assets. Future application of IFRS or equivalent standards in the Group’s accounting standards may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
(3) Risks related to asset management
-
① Market risk related to domestic interest rates
Because the Company’s asset structure has a high percentage of yen interest rate assets and the duration of the Company’s liabilities to policyholders is longer than the assets under management, the Company is exposed to the risk of fluctuations in domestic interest rates due to the mismatch between the duration of assets and liabilities.
Because the assumed interest rates on insurance policies already held by the Company has not changed even after the Bank of Japan lifted its negative interest rate policy in March 2024, if domestic interest rates rise above the level as of March 31, 2024, although interest income, etc. will improve due to higher investment yields, a decline in prices of bonds already held may result in valuation losses, impairment losses, or losses on sales.
On the other hand, if domestic interest rates fall below current levels, we may not be able to secure the investment returns we initially expected, or we may experience a negative spread (a phenomenon in which the average investment yield of the investment portfolio is less than the assumed interest rate used to accumulate policy reserves for existing policies). In this manner, fluctuations in domestic interest rates may affect the business, performance, and financial position of the Group.
-
② Market risks other than ① above
The Company holds assets denominated in foreign currencies, some of which are hedged by forward exchange contracts, etc. However, if fluctuations in foreign exchange rates occur with respect to the portion of foreign exchange risk that has not been hedged, or even if foreign exchange risk has been hedged, if hedging costs increase due to widening interest rate differentials between Japan and overseas caused by trends in monetary and fiscal policies in various countries, and if it becomes impossible to make forward exchange contracts, etc. by rolling under the existing conditions, the Group’s performance and financial position may be affected. In addition, changes in the monetary and fiscal policies of various countries and fluctuations in foreign interest rates could cause the value of our foreign securities holdings to decline, which could affect the performance and financial position of the Group.
Furthermore, if the prices of our stock holdings decline due to the deterioration of economic or market conditions in Japan or overseas or the emergence of geopolitical risks, our stock holdings may incur valuation losses, impairment losses, or losses on sales, which may affect the Group’s performance and financial position. In addition, deepening and evolution of asset management, such as alternative investment management, may not produce the expected results.
-
③ Credit risks
If the financial position of the Group’s business partners, investees or borrowers, or issuers of securities held by the Company deteriorates due to changes in domestic or overseas economic trends, changes in the business environment surrounding specific industries, the occurrence of scandals, the emergence of geopolitical risks, or other unforeseen circumstances, credit risk and credit-related costs may increase, or the value of our securities holdings may decline, which may affect the Group’s performance and financial position. In addition, achieving greater depth and evolution of asset management, such as management of foreign corporate and government bonds, may not produce the expected results.
In preparation for the above risks in ① through ③, the Company is continuing its efforts to enhance its ERM (enterprise risk management) that focuses on maintenance of financial soundness, and ALM (asset liability management) that controls risks while taking into account the balance between assets and liabilities, for the purpose of appropriately managing investment assets commensurate with the liabilities arising from underwriting insurance policies and stabilizing profit and loss. In addition, we regularly conduct stress tests to verify our ability to respond to the occurrence of stress events, and we are strengthening our screening and monitoring systems, especially in the deepening and evolution of asset management. However, if such responses are not successful, or if the market environment changes significantly due to domestic or international economic fluctuations or changes in monetary and fiscal policies of various countries, the Company’s performance and financial position may be affected.
(4) Risks related to market liquidity and funding
-
① Market liquidity risk
If the Group is unable to trade financial instruments and settle funds normally in the market due to disruptions in the financial markets, or is forced to trade at prices that are significantly less favorable than usual, the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be adversely affected. In addition, if market liquidity declines due to deterioration in domestic or overseas financial markets or economic conditions, the possibility of selling the Company’s holdings or their value may decrease.
-
② Funding risk
In the event that cash flow is tight due to an increase in payments of termination refunds following a large amount of policy surrenders and lapses or an increase in insurance claim expenditures following a significant natural disaster, and we are forced to sell assets at prices lower than the normal appraisal value to secure funds, or in the event that payment of insurance claims, etc. is delayed, it may affect the Group’s business, social credibility, performance, and financial position.
Ⅲ Business-specific
(1) Risks related to legal systems and regulations, etc.
-
① Risks related to laws and regulations under the Postal Service Privatization Act, etc.
The Company is under the supervision of the Financial Services Agency and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications in accordance with the Postal Service Privatization Act and related cabinet and ministerial orders. In addition, under the Postal Service Privatization Act, the Company is subject to the opinions of the Postal Privatization Committee operated by the Headquarters for the Promotion of Privatization of the Postal Services established by the Cabinet, as well as restrictive business regulations that are not imposed on other Japanese life insurance companies (hereinafter referred to as “additional restrictions,” details stated in “I. Company Overview, 3. Details of Business, (Reference) Special Measures under the Postal Service Privatization Act” of the 19th Annual Securities Report). If these regulations further restrict our competitiveness or revenue opportunities in the future, the Group’s business may be affected.
Japan, as a member of the WTO (World Trade Organization), has established a Protocol Amending the Agreement on Government Procurement, and the rules stipulated in this Protocol are applied to institutions that have succeeded to a public corporation, accordingly, when the Company procures goods, etc., it needs to comply with the government procurement rules under the WTO. If we fail to comply with these rules through our acts or omissions, procurement actions may not be concluded, or there may be delays in procurement actions, which may prevent us from implementing the plan we originally envisioned, thereby affecting the Group’s social credibility, performance, and financial position.
-
② Risks related to the Insurance Business Act and other related business regulations
The Company is a Japanese life insurance company, and like other Japanese life insurance companies, it is subject to supervision by the Financial Services Agency under the Insurance Business Act and related business regulations. The Insurance Business Act gives the Prime Minister (delegating authority to the Commissioner of the Financial Services Agency) broad supervisory authority over the insurance business, including the authority to revoke licenses, suspend operations, collect reports, and conduct strict on-site inspections regarding matters such as accounting records. In addition, the Commissioner of the Financial Services Agency is to conduct an examination if an application for approval or notification is made regarding the establishment of a new financial product or the revision of an existing product in accordance with the said Act.
The life insurance business license is the premise of the Company’s principal business activities, and the license does not expire, and as of March 31, 2025 the Company is aware of no events that would constitute grounds for revocation of the license. However, the occurrence of such an event could have an impact on the Company’s business activities.
In addition, in the event of violation of the Insurance Business Act or other particularly important laws and regulations, etc., the Company may be subject to administrative penalties such as suspension of all or part of its business operations or revocation of its license. Furthermore, if it becomes impossible to sell new products as planned in terms of content and timing, due to reasons such that the Financial Services Agency does not grant approval under the Insurance Business Act, or that such approval is not granted at the timing assumed by the Company, or if the expected revenue cannot be secured mainly due to external factors even after such approval is granted, it may affect the Group’s performance and financial position.
The Company is under the supervision of the Financial Services Agency based on the solvency margin ratio and real net assets, which the agency defines as indicators to judge the soundness of Japanese life insurance companies. The Company’s consolidated solvency margin ratio was 903.2% as of March 31, 2025, which is considerably higher than the legally regulated ratio. However, if the ratio falls below 200%, there is a possibility that the Prime Minister will take early corrective action, which may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
In addition, the IAIS (International Association of Insurance Supervisors) adopted the ComFrame (the Common Framework for Supervision of Internationally Active Insurance Groups (IAIGs)) in November 2019 and formally started applying the Insurance Capital Standard (ICS) for IAIGs, which is part of ComFrame, as regulatory capital requirements from 2025. The Financial Services Agency is also considering revising the current solvency margin regulation in Japan and introducing a new regulation with standards that align with the ICS in the fiscal year ending March 31, 2026. The regulation’s revised draft was announced on October 31, 2024 and January 31, 2025, respectively. The new regulations will be based on economic value and significantly differ from the current regulations. Changes and accompanying restrictions arising from the revision may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
-
③ Risks related to quality assurance in the insurance solicitation process
In response to the occurrence of the solicitation quality issues, the Group has prioritized and worked steadily to quickly regain the trust of customers and to ensure and improve solicitation quality by ensuring legal compliance and customer-first awareness in the insurance solicitation process.
However, with the increase in opportunities to interact with customers including elderly customers due to sales of lump-sum payment whole life insurance as well as the resumption of solicitation to elderly customers, if there are cases that are not in line with the wishes of customers and are disadvantageous, or that violate laws and regulations or internal rules, cases where the policy is not suitable for the customer or where the customer’s understanding of the policy is not sufficient even if it does not amount to a violation, or if complaints about insurance policies or requests for invalidation arise, the Group’s social credibility, performance, and financial position may be affected.
Accordingly, in the event that the Group is found to be in breach of its legal and regulatory obligations to be observed, depending on the scale and extent of such violations and our efforts, the Group may be subject to another administrative action, such as a business suspension order, from the supervisory authorities, which could have an impact on its management and the survival of its business. We will further deepen our understanding of the underlying causes of such incidents, as the improper handling of non-public financial information, and the solicitation for the sale of lump-sum payment whole life insurance before regulatory approval required under the Insurance Business Act, in order to ensure the effectiveness of measures to prevent recurrence, as well as to work to ensure and improve the quality of the insurance solicitation process, thereby ensuring legal and regulatory compliance and thorough implementation of customer-oriented activities.
(2) Risks related to the relationship with Japan Post Co., Ltd.
-
① Risks related to provision of universal service
In order to comply with the provisions for universal service under the Postal Service Privatization Act, Japan Post Co., Ltd. has entered into a life insurance sales and maintenance agreement and a life insurance counter services agreement with the Company and is entrusted with the Company’s insurance agency business, and provides the Company’s products and services at each post office nationwide (details stated in “5. Important Contracts” of the 19th Annual Securities Report).
In particular, the life insurance counter services agreement is a contract with no fixed term and cannot be unilaterally terminated by the Company unless there are special circumstances stipulated in the contract. In addition, there is a provision in the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to the effect that the Company shall enter into a life insurance counter services agreement with Japan Post Co., Ltd., and if such agreement is terminated, an amendment to the Company’s Articles of Incorporation will be required. Accordingly, in order for the Company to terminate the life insurance counter services agreement with Japan Post Co., Ltd., it is necessary to follow these procedures and others.
In this manner, the Company has a contractual obligation to maintain its status as an affiliated insurance company in providing universal service by Japan Post Co., Ltd., and as a result, the Company’s flexible business development could become difficult.
In addition, the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be affected by future government measures to ensure universal service, as well as amendments to laws and regulations.
Due to the enforcement of the Act to Partially Revise the Act on the Management Organization for Postal Savings and Postal Life Insurance in December 2018, of the costs required to maintain the post office network, which were previously covered by consignment commission based on contracts between Japan Post Co., Ltd. and affiliated banks and insurance companies, in accordance with the act, the essential costs for ensuring universal service (excluding the amount to be borne by Japan Post Co., Ltd.) are covered by a grant to Japan Post Co., Ltd. by the Organization for Postal Savings, Postal Life Insurance and Post Office Network (hereinafter referred to as the “Management Network”) with contributions from the Company and Japan Post Bank Co., Ltd. starting from the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020.
Such essential costs constituting the basis for the calculation of the amount of contribution/grant are calculated as the sum of the following costs based on the most recent status of maintenance of the post office network.
- A. Personnel expenses, rent, construction expenses and other expenses necessary to maintain post offices, expenses necessary for transporting and managing cash, property taxes and business facility taxes, in each case, based on a post office network consisting of post offices of the minimum scale necessary to operate the network; and
- B. Expenses necessary for the minimum level of outsourcing services needed to ensure that basic postal services can be provided at contracted post offices
The contributions paid by the Company to the Management Network (56.3 billion yen paid by the Company for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2025) are the portion allocated to insurance counter operations of the total amount of such essential costs and the Management Network’s administrative costs related to the calculation of contributions and grants, which is divided proportionally between the postal counter operations, bank counter operations, and insurance counter operations, according to their expected degrees of use of the post office network.
In this manner, our contributions are calculated by the Management Network in accordance with the relevant laws and regulations, and therefore do not reflect the Company’s intentions.
As an affiliated insurance company of Japan Post Co., Ltd. in providing universal service, we are required to make this contribution, which is a fixed operating expense unique to the Company. If the amount of such essential costs calculated by the Management Network is larger than we anticipate, the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be affected.
Based on a life insurance solicitation and policy maintenance and operation services consignment agreement and an insurance counter services agreement concluded with Japan Post Co., Ltd., the Company is responsible for the agency management as the entrusting party. Under such circumstances, in addition to the improper handling of non-public financial information within the Japan Post Group, an incident involving solicitation for the sale of lump-sum payment whole life insurance product before obtaining the regulatory approval required under the Insurance Business Act was also identified. Going forward, we will further deepen our understanding of the underlying causes of these incidents, ensure the effectiveness of measures to prevent recurrence as well as of the agent management system in outsourcing services in general as the manager of agencies. However, if the Company’s agency management system does not function effectively or defects occur, the Group may suffer unexpected losses or be subject to administrative dispositions, etc., which may affect the Group’s social credibility, business, performance, and financial position.
-
② Risks related to consignment commission, etc. paid to Japan Post Co., Ltd.
Based on a life insurance sales and maintenance agreement and a life insurance counter services agreement, etc. signed with Japan Post Co., Ltd., as well as agent commission arrangements, etc. notified to Japan Post Co., Ltd., the Company pays consignment commission to Japan Post Co., Ltd. The commission includes those calculated by multiplying the unit cost of the services provided by Japan Post Co., Ltd. to the Company by the number of post offices, etc., and those required for the maintenance and management of policies in force, which include fixed operating expenses that are incurred independent of the volume of sales activity and may not be reduced immediately, and expenses may increase depending on work outsourced from the Company.
In addition to the above, the Company may consider introducing a commission consistent with the Group’s business strategy for each fiscal year. Failure to properly set up a consignment commission structure, including such commission, could damage the credibility of the Group, and could affect the actual result in terms of new policies or the maintenance of policies in force, as well as its business performance and financial position (details stated in “5. Important Contracts, (Reference) Consignment Commission Paid to Japan Post Co., Ltd.” of the 19th Annual Securities Report).
-
③ Risks related to the post office network
Although the majority of the Company’s products and services are provided through the post office network, recently, the diversification of means of communication has made various services necessary for daily life easily accessible via means such as the Internet, and the need for non-face-to-face services has increased. If the sales capabilities and attractiveness of the post office network is impaired due to a decrease in the number of post offices and the number of users or frequency of use of post offices as a result of these factors, the actual result of the Company’s new policies and maintenance of policies in force may be adversely affected. The Company will continue to consider and introduce means of providing products and services that complement or partially replace the post office network. However, if these measures are not successful, the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be affected.
In addition, the provision of our products and services at post offices is performed by employees of our contractor, Japan Post Co., Ltd. For this reason, if securing excellent personnel by Japan Post Co. Ltd. or our training for Japan Post Co. Ltd. employees in the insurance business, etc. is not adequate, there is a possibility that the Company’s products and services may not be provided as expected.
(3) Risks related to the relationship with Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
-
① Risks related to influence and conflicts of interest with other general shareholders due to the holding of voting rights by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
Although Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. holds 49.8% of the Company’s voting rights as of March 31, 2025 Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. may still have influence on the outcome of resolutions of the Company’s general meeting of shareholders, such as the election and dismissal of the Company’s directors, organizational restructuring such as mergers with other companies, capital reduction, and amendments to our Articles of Incorporation. Furthermore, as of March 31, 2025, the Japanese government holds approximately 38.8% of the voting rights of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
From the perspective of the interests of the Japan Post Group and the provision of universal service, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. may exercise voting rights, etc. that are different from the interests of the Company and its general shareholders. In addition, as described in “b. Transactions with the Japan Post Group” below, in addition to having a business contracting relationship and other transactional and contractual relationships with the Company, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. has interests that differ from those of the Company’s general shareholders, such as engaging in businesses that compete or may compete with the Company through its subsidiaries, etc. (commissioned sales of products of life insurance companies other than the Company, etc.). For example, in December 2018, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. entered into a basic agreement with Aflac Incorporated and Aflac Life Insurance Japan Ltd. regarding a Strategic Alliance Based on Capital Relationship. Based on this agreement, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. acquired 7% (as of December 2018) of the total number of Aflac Incorporated’s common shares issued, reaffirmed its commitment to cancer insurance, and discussed new collaborative initiatives, and in June 2021, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd., Japan Post Co., Ltd., and the Company agreed to further develop the Strategic Alliance Based on Capital Relationship with Aflac Incorporated and Aflac Life Insurance Japan Ltd. In March 2024, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. applied the equity method to Aflac Incorporated, and a portion of Aflac Incorporated’s profits is reflected in the consolidated results of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. from FY2024. In addition, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. entered into a business alliance agreement with Japan Post Co., Ltd. and Rakuten Group, Inc. to strengthen cooperation in various areas such as logistics, mobile, and DX in March 2021. Furthermore, in April 2021, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd., Japan Post Co., Ltd., Japan Post Bank Co., Ltd., and the Company signed a business alliance agreement with Rakuten Group, Inc. once again. In these agreements, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. will discuss and consider collaboration in the insurance field, but the details of the collaboration may conflict with the interests of the Company and its general shareholders, such as affecting the Group’s performance.
Personal and business relationships between the Company and the Japan Post Group are as follows.
-
- a. Risks related to personal and business relationships with the Japan Post Group
The Company has directors who concurrently serve as directors/executive officers of the Japan Post Group, and the table below shows the main directors who concurrently serve as directors/executive officers of the Japan Post Group as of the date of submission of the 19th Annual Securities Report. In principle, except for members of the Executive Committee who concurrently serve as executive officers of the Company at the managing executive officer level or above and as executive officers of the Company who are in charge of business operations, no directors or executive officers of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. attend the Company’s Executive Committee meetings. However, the Company requests representative executive officers of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. to attend the meetings when we consider their attendance necessary depending on the agenda or matters to be reported.
Name Position in the
CompanyMain positions in the
Japan Post GroupReason for concurrent
appointmentTANIGAKI Kunio Director and President, CEO, Representative Executive Officer Director (part-time) of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. To enhance the effectiveness of business management and management efficiency of the Group ONISHI Toru Director and Deputy President, Representative Executive Officer Managing Executive Officer (part-time) of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. To respond to technical questions about the Company in the Diet as Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd., a corporation in which the government invests more than one-third of its capital MASUDA Hiroya
(Note)Director
(part-time)Director and Representative Executive Officer, President & CEO of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. To strengthen Group governance scroll
(Note) He serves concurrently as a Director (part-time) of Japan Post Co., Ltd. and Japan Post Bank Co., Ltd., subsidiaries of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
The Company has proposed an election of 11 Directors as the proposal (matters to be resolved) at the Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders to be held on June 18, 2025. If the said proposal is approved, the main directors who will concurrently serve as directors/executive officers of the Japan Post Group will be as shown in the table below.
Name Position in the
CompanyMain positions in the
Japan Post GroupReason for concurrent
appointmentTANIGAKI Kunio Director and President, CEO, Representative Executive Officer Director (part-time) of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. To enhance the effectiveness of business management and management efficiency of the Group ONISHI Toru Director and Deputy President, Representative Executive Officer Managing Executive Officer (part-time) of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. To respond to technical questions about the Company in the Diet as Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd., a corporation in which the government invests more than one-third of its capital NEGISHI Kazuyuki
(Note)Director
(part-time)Managing Executive Officer of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. To strengthen Group governance scroll
(Note) He will be appointed as Director and Representative Executive Officer, President & CEO of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd., which is the Company’s parent company, and Director (part-time) of Japan Post Co., Ltd. and Japan Post Bank Co., Ltd., subsidiaries of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
The status of the Company’s directors is as described in “IV. Status of Submitting Company, 4. Corporate Governance, etc., (2) Status of Directors” of the 19th Annual Securities Report.
Although the Company accepts seconded employees and conducts personnel exchanges with Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. and its subsidiaries, Japan Post Co., Ltd. and Japan Post Bank Co., Ltd., none of these employees holds a position that has a significant impact on the Company’s business operations.
- b. Transactions with the Japan Post Group
The Company conducts transactions with other companies belonging to the Japan Post Group, and the main transactions in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2025 are as follows.
Details of transaction Counterparty Amount
(Millions of yen)Method of determining transaction terms, etc. Payment of brand royalty fees Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. 1,951 As described below in “② Risks related to brand royalty fees to Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.” Payment of system usage fees Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. 2,062 The Company, Japan Post Co., Ltd., and Japan Post Bank Co., Ltd. bear an amount calculated by multiplying the necessary expenses for providing the system by a certain profit margin ratio set in consideration of the profit margin ratio of other companies, depending on the usage of the system, etc. Payment of consignment commission for agency services Japan Post Co., Ltd. 111,436 The Company makes payments including sales commission calculated by multiplying the insurance amounts and the insurance premiums of each contract by the commission rates set for each class of insurance, and maintenance commission calculated by multiplying the unit prices set for each type of outsourcing services, such as the collection of insurance premiums and payments for insurance claims, by the number of policies in force. Postage and other charges Japan Post Co., Ltd. 5,259 Postage is charged at the same rate as general customers in accordance with our policy agreements. Lease of building owned by Japan Post Co., Ltd. Japan Post Co., Ltd. 7,247 Rent (including Common Area Maintenance charges) is set using a method similar to the cost approach for rental valuation, thereby ensuring its appropriateness. Payment of counter terminal usage fees Japan Post Bank Co., Ltd. 1,280 The Company and Japan Post Bank Co., Ltd. set the share according to the number of terminal operations handled, and the Company pays an amount corresponding to its share of the maintenance costs of the counter terminals. scroll
(Note) In addition to the above, as described in “III Business-specific, (2) Risks related to the relationship with Japan Post Co., Ltd., ① Risks related to provision of universal service,” there was a payment of 56.3 billion yen in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2025 for contributions to the Management Network in relation to the maintenance of the post office network.
In order to ensure the appropriateness of transaction terms with other companies belonging to the Japan Post Group, the Company has established a system whereby resolutions are passed at meetings of the Board of Directors, including outside directors, when new important transactions are implemented, or existing important transaction terms are changed.
- a. Risks related to personal and business relationships with the Japan Post Group
-
② Risks related to brand royalty fees to Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
As stated in “5. Important Contracts” of the 19th Annual Securities Report, the Company has concluded the Japan Post Group Agreement and other agreements with each company in the Japan Post Group, and matters necessary for the appropriate and smooth operation of the Group or matters requiring management by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. under laws and regulations are subject to prior consultation with Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. or reporting to Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. In addition, the Company is licensed by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. to use “Kampo Seimei” and other trademarks, and pays brand royalty fees to Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. as consideration for the benefit of being able to utilize the brand power of the Japan Post Group in the Company’s business activities.
Based on the concept that the brand value from which we benefit by belonging to the Japan Post Group is reflected in our business performance, this fee is calculated by multiplying the amount of insurance policies in force as of March 31, 2024, a performance indicator that reflects such benefit, by a certain rate (0.0036%), and this rate will not be changed unless there is a significant change in economic conditions or other special circumstances. The brand royalty fees will continue to be paid as long as the Company belongs to the Japan Post Group, and the obligation to pay such royalty fees will continue as long as the Company operates as an affiliated insurance company as defined in the Act on Japan Post Co., Ltd., regardless of the percentage of the Company’s shares held by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
If the Company is no longer able to use the trademark under the conditions as of March 31, 2025 due to the termination or revision of these agreements, etc., or if the calculation method of brand royalty fees is changed due to significant changes in economic conditions or other special circumstances, the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be affected.
-
③ Risks related to additional disposal of the Company’s shares by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
While the percentage of the Company’s voting rights held by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. is 49.8% as of March 31, 2025 under the Postal Service Privatization Act, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. aims to dispose of all of the Company’s shares held by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. as soon as possible, taking into consideration the Company’s business situation and the impact on the provision of universal service, and Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. has announced that it will continue to consider the disposal of shares in the Company even after its shareholding ratio falls below 50%.
In accordance with the Postal Service Privatization Act, the Company is subject to additional restrictions that other companies in the industry are not. However, such restrictions will cease to apply when (i) Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. disposes of all of its shares in the Company, or (ii) Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. disposes of one-half or more of its shares in the Company, and the Prime Minister and the Minister of Internal Affairs and Communications recognize that there is no risk of impeding appropriate competitive relationships with other financial institutions and appropriate provision of services to users and determine that the additional restrictions do not apply to the Company. Although Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. has notified the Minister of Internal Affairs and Communications that it has disposed of more than one-half of the Company’s shares, because of the discretion of the authorities in determining (ii) above, it is unclear when and how the additional restrictions will be removed. Among the additional restrictions, the restrictions on operations stipulated in Article 138 of the Postal Service Privatization Act, such as approval for the development of new products and implementation of new asset management methods, will not apply after the day Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. notifies the Minister of Internal Affairs and Communications that it has disposed of more than one-half of the Company’s shares, and the Company has already shifted to a notification system. Although the timing and scale of any future sale of our shares by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. have not yet been determined, if additional sales of our shares are made in the future, or if there is a widespread perception in the market that such sales will increase the number of our shares circulating in the market and worsen the supply-demand balance, the liquidity of the Company’s shares and the formation of the Company’s stock price may be affected. Conversely, if the further sale of our shares by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. does not proceed as planned due to changes in the provisions of the Postal Service Privatization Act concerning the disposal of the Company’s shares, stock market trends, or other factors, the removal of the additional restrictions may not take place, and the expanded management flexibility that Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. and the Company expect may not be realized.
In addition, if the terms and conditions of the life insurance solicitation and policy maintenance operations consignment agreement, the insurance counter operations agreement, or any other agreements that the Company has concluded with Japan Post Co., Ltd. are changed to the Company’s disadvantage or if such agreements are terminated as a result of the sale of the Company’s shares by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd., a large amount of cost, time, etc. may be required to maintain our business as before due to such factors as inability to use the post office network, which may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position. In addition, with respect to the Japan Post Group Agreement and the Japan Post Group Trademark Management Agreement that the Company has concluded with the Japan Post Group, as well as the Agreement Relating Japan Post Group Management and the Group Trademark Management Agreement that the Company has concluded with Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd., if the Company ceases to be an affiliated insurance company and an agreement or contract itself is not applied, the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be affected.
Furthermore, although the Company has not received any guarantee or other credit enhancement from the Japanese government or any other public institution, in the event that the misconception or illusion that the Company’s economic creditworthiness has declined is widely propagated in society as a result of Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd. ceasing to be the Company’s parent company, this could have a negative impact on employee recruitment activities, induce customers and other business partners to suspend transactions, reduce transaction volume, cancel insurance contracts, or change terms and conditions of transactions to those that are unfavorable to the Company.
Ⅳ Operation
(1) Operational risks
-
Operational risk (including compliance risk) exists in the course of the Group’s business operations and may include internal and external misconduct, occurrence of problems in labor management and workplace environment, loss of credibility due to inadequate response to customer-first business operations, business interruption due to system failure, etc., inappropriate paperwork, inadequate payment of insurance claims and other payments, pressures on administrative systems, inadequate trademark applications and other administrative matters. In particular, because most of the Company’s products and services are provided through the post office network, where not only our business but also banking and logistics services are provided in parallel, the possibility of these operational risks materializing is relatively high, which may affect our business, social credibility, performance, and financial position.
-
① System risks
The Group conducts life insurance solicitation and management operations using not only the systems owned by the Group, but also those owned by Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd., Japan Post Co., Ltd., and Japan Post Bank Co., Ltd, and the information system performs an extremely important function for the Company’s business, as it communicates with post offices nationwide and with the Company’s various offices, etc.
In addition to external factors such as earthquake, eruption, tsunami, typhoon, flood, heavy snowfall, fire, and other natural disasters and terrorism, such information systems may experience serious failures or malfunctions due to human error, accidents, power outages, defects in new system development and updates, and defects in service provision by telecommunications carriers and other third parties. In the event of such a system failure or malfunction, the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be affected due to the suspension or disruption of operations and the resulting compensation for damages, administrative penalties, damage to social credibility, and costs incurred in responding to or taking countermeasures against such events.
-
② Risks related to cyberattacks
While service provision to customers is further increasing due to the promotion of DX and utilization of AI, cyber risks are becoming more serious every year as cyberattack methods against systems are becoming more advanced, sophisticated, and systematized every day. In addition, such risks may further increase in the future due to geopolitical risks associated with changes in social conditions and risks from supply chains via third-party systems such as contractors.
In light of such risks, we have established a prevention system based on the concept of multi-layered defense, which combines defense and detection mechanisms, and a system to take appropriate measures to prevent the spread of damage by the Japan Post Insurance CSIRT (Computer Security Incident Response Team), a specialized security organization, in the event of a cyberattack. Moreover, we are further strengthening our information security management system by enhancing data governance in consideration of economic security, ensuring the proper business operation framework in compliance with laws and regulations, enhancing information asset management, and strengthening supply chain risk countermeasures, as well as improving company-wide information literacy and thoroughly implementing information management rules as the foundation for these efforts. In addition, to prepare for any event of crises resulting from cyberattacks, we are working to ensure the effectiveness of the crisis management measures applied when performance becomes difficult under the regular business execution framework, external correspondence to customers and other parties, and business continuity measures with alternative means by establishing them in advance and through training and drills.
In this manner, we are constantly working to improve our cyber security measures. However, in spite of these measures, if our information system were to fail due to an unknown threat that significantly affects our business, the time and cost required to investigate and analyze the extent of the impact, restore the system, and prevent its recurrence, could affect the Group’s business, social credibility, performance, and financial position.
-
③ Risks related to compliance
The Group is under the supervision of the Financial Services Agency and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications in accordance with the Insurance Business Act and the Postal Service Privatization Act. In addition, as a business that handles life insurance policies, the Group is obligated to comply with various related laws and regulations, including the Insurance Act, the Consumer Contract Act, the Act on the Protection of Personal Information, and the Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds.
Based on our reflection on the solicitation quality issues, etc., the Group defines compliance risk as the risk of losing the trust of customers and other stakeholders due to acts that violate social expectations, such as acts that lack the user perspective, as well as compliance with laws and regulations, resulting in damage to corporate value, and is reinforcing its risk management system by strengthening cooperation between the risk management and compliance departments. Through these initiatives, we will detect risk information with a high level of risk sensitivity, and by instilling in each employee the behavior that meets society’s expectations, we will curb the manifestation of compliance risks in the insurance solicitation process and in all other business operations.
Furthermore, we have formulated a code of conduct based on our customer-first philosophy, and are implementing company-wide efforts to further strengthen compliance, including offering training programs to ensure that the code of conduct permeates the sales floors of post offices and other locations. However, if these guidance and education are not sufficiently effective or if other violations of laws and regulations, such as inappropriate solicitation activities, occur, the Group’s social credibility, business, and performance could be affected.
In addition, the Group has established a Compliance Program up until now to ensure compliance with laws and regulations through regular compliance training for executives and employees, thorough information management, and strengthening of measures against crime prevention, anti-money laundering, combating the financing of terrorism, and countering proliferation financing. However, the occurrence of violations of laws and regulations due to acts or omissions by executives or employees, or the ineffectiveness of measures taken to prevent violations of laws and regulations, may affect the social credibility and business of the Group. In addition, although the Company has entered into a vast number of insurance policies and contracts for operations consignment and purchase of goods, in the event that the Company is the victim of fraudulent acts by the other party to the contract, or if it enters into a contract with antisocial forces, the social credibility and business of the Group may be affected. Furthermore, the Group is exposed to the risk of potential losses due to fraud and other forms of misconduct by its employees, agents, contractors, and policyholders. The Company’s employees and agents hold personal information of policyholders through their interactions with policyholders, and we cannot deny the possibility that illegal sales techniques, fraud, identity theft, loss or leakage of personal information, or inappropriate use of such information may occur. Although we take measures to prevent or detect such illegal activities, if our initiatives fail to eliminate them, the social credibility and business of the Group may be affected.
In this manner, the Group is subject to various regulations such as the Insurance Act and the Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds, and any revision of such regulations or change in government policy regarding their enforcement may result in new responses, costs, etc., which may affect the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
-
④ Risks related to information leakage
In the course of its business, the Group acquires and holds a large amount of information directly from the Company or through its agent, Japan Post Co., Ltd. This information includes information on individual customers and corporate customers, such as policyholders, as well as various internal information obtained in the course of business. Among this information, personal information (including Individual Numbers as defined in the “Act on the Use of Numbers to Identify a Specific Individual in Administrative Procedures”; the same applies below) is required to be handled appropriately in accordance with the Act on the Protection of Personal Information and other related laws. In particular, leakage and loss of personal information held by companies and organizations have frequently occurred recently, and stricter management is required for such information.
The Group has established a privacy policy and rules and regulations for information management in an effort to ensure strict information management. In addition, as part of its work style reform efforts, the Group is promoting work from home, and is also thoroughly promoting information management awareness.
However, in the event that personal information or other important information held by the Company is leaked to outside parties by employees (including retired employees), agents, contractors, or other parties, and the Company is subject to claims for damages, administrative investigations, guidance, or disciplinary action, the Group may incur time and costs to deal with the matter, or lose its social credibility, which may affect the Group’s performance and financial position.
-
⑤ Risks related to lawsuits, administrative actions, etc.
The Group is exposed to the risk of lawsuits and other legal proceedings being brought or initiated against it in connection with the execution of its business. In addition, there is a possibility that lawsuits may be filed by policyholders, etc., or that lawsuits related to personnel treatment, work management, harassment, and other personnel and labor issues, or workplace health and safety management issues, etc., may be filed by the Group’s employees or others.
If a new lawsuit is filed against the Company, it may take a considerable amount of time and cost to resolve the lawsuit. In the event that a lawsuit or other legal action over an event of significant social interest or impact is initiated, and adverse decision such as an order requiring the Company to pay damages was made, the Group’s social credibility, business, performance, and financial position may be affected.
-
⑥ Risks related to rumors, false information, etc.
In the event that rumors and false information about the Group’s business in general spread through the media, market participants, and postings on Internet bulletin boards and social media, and negative media reports are made by the media, or misinformation such as fake news disseminates through the misuse of AI and reputational risks materialize, etc., against the backdrop of public benefit, business scale, and recognition and visibility in society of the Group’s services, and regardless of whether such rumors, false information, and media reports are based on fact or not, they may be negatively understood, perceived, or strongly criticized by customers, market participants, etc., which may further damage the image and social credibility of our products, services, and business, thereby affecting the Group’s business, performance, and financial position.
(2) Risks related to the effectiveness of risk management
-
The Group has established rules of risk management and has a risk management framework to manage insurance underwriting risk, asset management risk, market liquidity risk, funding risk, and operational risk in general.
Although the Group’s management of risks including insurance underwriting risk, asset management risk, market liquidity risk, and funding risk is built on our past experience and data, it is not necessarily possible to accurately predict risks that may arise in the future, and thus risk management may not function effectively due to the Group’s entry into new business fields or changes in the external environment. In addition, the information used as reference or assumed by the Group in formulating risk management policies and procedures may lack accuracy, completeness, or rationality.
Furthermore, although the effectiveness and efficiency of policies and procedures related to the proper recording, review, and investigation of a vast number of transactions and events are critical to managing the risks in the Group such as operational risk, such policies and procedures may not necessarily function effectively in the future. Moreover, the implementation of risk management and supervision of its compliance must be conducted across the entire post office network of Japan Post Co., Ltd., which provides the Company’s products and services. If there are difficulties or failures in the implementation and supervision of risk management to the post office network including offering of products of Japan Post Bank Co., Ltd. and the postal and logistics services of Japan Post Co., Ltd., risk management by the Company may not function or may be insufficient.
The Company reviews its overall risk management system from time to time in response to changes in the business environment, risk conditions, and other factors, and strives to establish a complete risk management system. However, if the Group’s risk management system does not function effectively or defects occur, the Group may suffer unexpected losses or be subject to administrative dispositions, etc., which may affect the Group’s social credibility, business, performance, and financial position.
Ⅴ Others
(1) Risks associated with the occurrence of largescale natural disasters, etc.
-
The Company operates a life insurance business with a nationwide sales network in Japan. Accordingly, in the event of a large-scale disaster such as an earthquake, eruption, tsunami, typhoon, flood, or heavy snowfall; a pandemic of infectious diseases such as a new type of influenza; a human disaster such as terrorism or a conflict between nations; or a major failure or disruption of social infrastructure such as water, electricity, gas, telecommunications, or financial services, the following situations may occur.
- ・Insurance claims payments or policy cancellations exceeding initial expectations
- ・Decrease in premium revenue due to fewer insurance sales opportunities and lower insurance needs
- ・Damage to the value of stock holdings and other assets due to stagnation of economic activities caused by the issuance of voluntary restraints on going out due to the spread of large-scale infectious diseases and increased risk aversion in the financial markets
- ・Difficulties in ensuring normal business operations, such as suspension or stagnation of business due to the damage or illness of executives, employees, and related persons, or a decrease in the number of employees coming to work to prevent the spread of the disaster, as well as expenses incurred for business continuity and recovery
- ・Suspension or stagnation of operations due to damage to the Group’s head office, branches, or other equipment and facilities, and incurrence of expenses for business continuity and restoration
- ・Losses incurred due to the establishment of special treatment or services based on factors such as social demands in an emergency, and the occurrence of cases of application beyond initial assumptions
In addition to accumulating contingency reserves in accordance with the standards of the Insurance Business Act in preparation for payment of insurance claims, the Company strives to ensure sufficient fund liquidity. In addition, we have formulated a business continuity plan to ensure that, in the event of an emergency, we can reliably carry out important operations such as payment of insurance claims as an insurance company. We hold regular liaison meetings of crisis management officers and conduct disaster drills from normal times to raise awareness of crisis management among executives and employees, and confirm the status of our response to disasters. Furthermore, the Crisis Management Committee plays a central role in the Company’s system to take appropriate and prompt action in the event of a crisis.
However, if such responses are not successful, or if a disaster beyond expectations occurs and the aforementioned events occur, expand, or become prolonged, the Group’s business, performance, and financial position may be affected.
Relate starts here.